Understanding Sciatica: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
What is Sciatica?
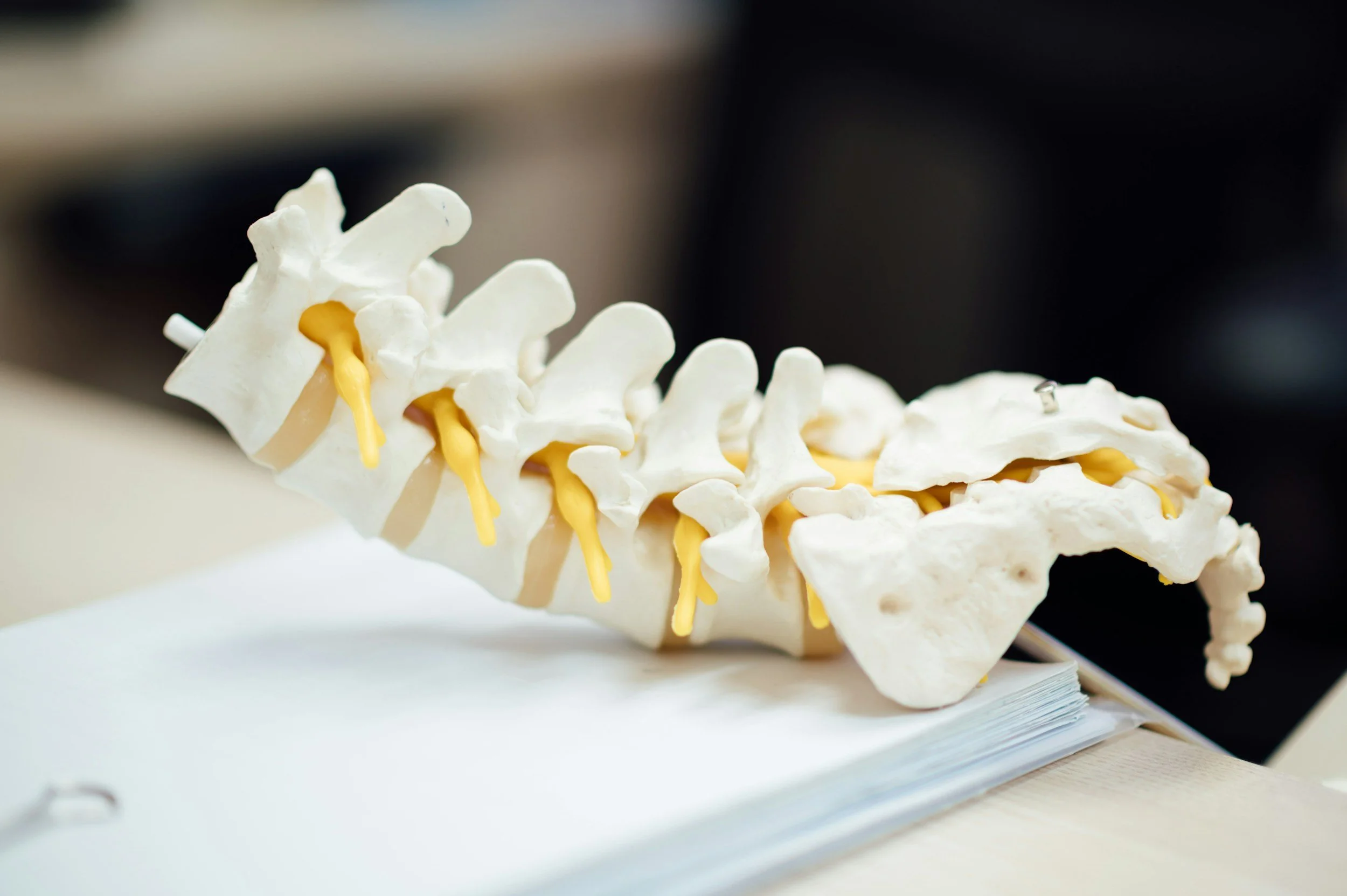
Sciatica is a condition characterized by pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which branches from your lower back through your hips and buttocks and down each leg. Typically, sciatica affects only one side of your body.
Herniated Disc: A slipped or herniated disc in the spine pressing on the nerve.
Bone spurs: An overgrowth of bone can compress on the nerve root.
Degenerative Disc Disease: Wear and tear on the spinal discs.
Spondylolisthesis: A condition where one vertebra slips forward over another.
Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal. More common as we age.
Piriformis Syndrome: Irritation of the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle in the buttock.
Causes of Sciatica:
Sciatica occurs when the sciatic nerve is compressed, irritated, or inflamed. Common causes include:
Pain: Sharp, burning, or shooting pain that radiates from the lower back to the leg, in some cases into the heel, foot and toes.
Numbness: Loss of sensation or tingling in the leg or foot. Occasional a pins and needles sensation.
Weakness: Difficulty moving the leg or foot.
Lower Back Pain: Pain in the lumbar region of the spine.
Buttock Pain: Sharp pain that can feel deep into the buttock muscles,
Symptoms of Sciatica:
Sciatica can cause a range of symptoms, which may vary in intensity:
How Osteopathy Can Help Sciatica?
Osteopathy offers a holistic approach to treating sciatica. Here’s how we can help:
Assessment:
In the first session an Osteopath will take a comprehensive evaluation of your condition, including posture and movement analysis. Questions about the pain including onset, duration, characteristics will be asked, and a deeper medical history evaluation may take place to gain a true understanding of how the injury may have occurred.
Diagnosis:
Osteopaths then form a diagnosis, which dictates a treatment plan, rehabilitation exercises and education to help you manage your injury.
Treatment:
Hands-on techniques to improve mobility, relieve pain, and promote healing. These may include:
Spinal Manipulation: Gentle adjustments to relieve pressure on the sciatic nerve.
Soft Tissue Therapy: Massage and stretching to alleviate muscle tension.
Exercise and Education:
Exercise Prescription: Personalised exercises to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
Lifestyle Advice:
Exercise modification - This could be modifying the quantity, intensity or duration of your exercise to help ease any aggravating factors contributing to injury.
Stay Active: Regular, low-impact exercises such as walking or swimming.
Practice Good Posture: Maintain proper posture when sitting, standing, and lifting.
Use Proper Ergonomics: Ensure your workspace is set up to support your back.
Stretch Regularly: Perform stretches to keep your muscles flexible.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can increase pressure on your spine.
FAQs for Sciatica
-
Sciatica refers to pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which runs from your lower back through your hips and buttocks and down each leg. It usually affects only one side of the body.
-
While not all cases can be prevented, you can reduce your risk by:
Regular Exercise: Engage in low-impact activities like walking or swimming.
Proper Posture: Maintain good posture when sitting, standing, and lifting.
Ergonomic Workspace: Ensure your work environment supports good posture.
Stretching: Regularly stretch to keep muscles flexible.
Healthy Weight: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce spinal pressure.
-
Sciatica can vary in duration:
Acute Sciatica: Typically lasts 4 to 6 weeks.
Chronic Sciatica: Persists for longer periods and may require ongoing management.
-
Treatment options include:
Osteopathy: Spinal manipulation, soft tissue therapy, and personalised exercises.
Medication: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, and muscle relaxants.
Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve strength and flexibility.
Lifestyle Changes: Posture correction, ergonomic adjustments, and weight management.
Surgery: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail.
-
Seek medical attention if you experience:
Severe or worsening pain despite self-care measures.
Pain following a significant injury.
Difficulty controlling your bladder or bowels.
Significant weakness or numbness in your leg.
-
IteYes, but it's important to:
Choose Low-Impact Activities: Such as walking, swimming, or cycling.
Avoid Aggravating Movements: Steer clear of activities that worsen your pain.
Follow Professional Guidance: Work with your osteopath or physical therapist to develop a safe exercise plan.m description
Where can I get more information or treatment for Sciatica?
For more information or to schedule a consultation, contact us to speak with one of our experienced osteopaths. We’re here to help you find relief and improve your quality of life.